Not only can SEO seem like a dark art but it’s also full of jargon and acronyms that make it seem totally inaccessible to most of us.
However, this is worth knowing about. Schema markup (also called structured data) is one of those small tweaks that can make a big difference to how your website appears in search results – and how many people click on it.
Let’s explore the details.
More about schema markup
Schema is a bit of behind-the-scenes code you can add to your website. It tells search engines exactly what a page is about - clearly and in their language. Imagine your website as a market stall. Schema is the label that says: “Organic vegan candles, handmade in Cornwall. £15 each. Free delivery.” All the key information and no guessing required.
To search engines, a regular page is just a stream of text. Schema adds clarity, giving specific details to the search engine. It marks up that a review is a review, an event is an event, or a product is a product - with details like price, availability, and rating.
Why does it matter?
Schema markup can make your search listings look more appealing and more useful. They can show more information, which gets more attention and more clicks. Search engines sometimes reward schema by showing “rich results”, which are the extras you see in search listings. Examples are stars next to product reviews, FAQ dropdowns, event dates, recipe images, product prices and “People Also Ask”. Rich results don’t just look nicer - they take up more space in search results, which can push your competitors further down the page.
Does schema boost your rankings?
Not directly. According to Google, schema isn’t a ranking factor. But it can improve click through rates - which is a signal search engines take into account. More clicks = more interest = more trust.
Crucially, it also helps AI search tools understand your pages better. This matters more and more as search becomes increasingly conversational.
What kinds of schema can you use?
Here are a few practical ways small businesses might use it:
- FAQ schema: Adds collapsible Q&A sections in your search result. Great for customer service and SEO at once.
- Product schema: Highlights product details – price, availability, reviews. Especially good if you sell online.
- Article schema: Helps Google display your blog posts correctly, with a clear headline and author.
- Local business schema: Tells search engines your business name, address, phone number, and opening hours. Essential for bricks-and-mortar businesses.
- Event schema: Adds date, location, and ticket links to events you’re running – whether it’s a workshop, pop-up or launch.
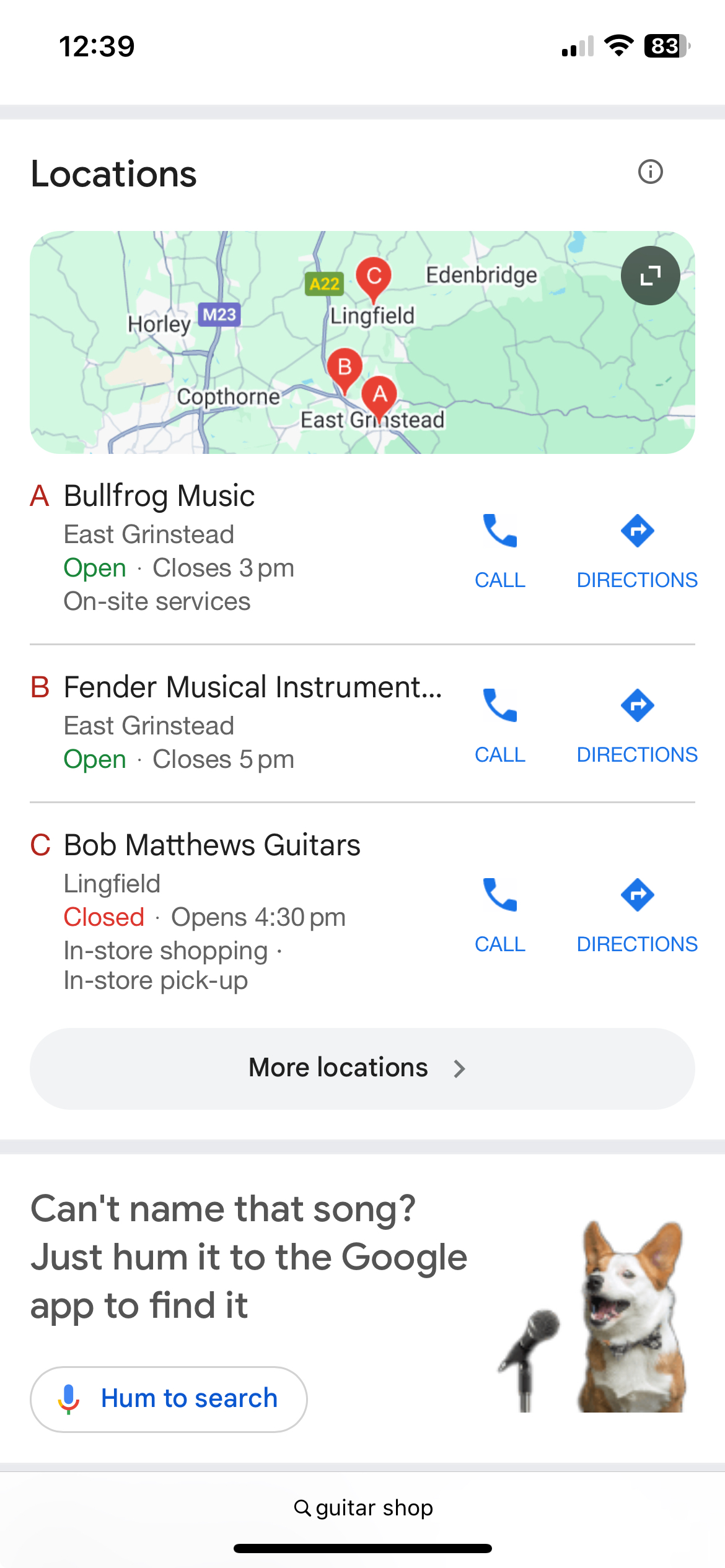
Local schema
If you have a physical shop, studio, or workspace - even if it’s just by appointment - local business schema is a must.
It helps search engines understand where you are, what you do, and when you’re open. This makes it much easier to show up when someone nearby searches for your kind of service or product.
Even better, it can boost your visibility in Google’s “Snack Pack” – that little map section with three local business listings that pops up when someone searches for something like “guitar shop near me” or “cardboard packaging Brighton”.
Getting into the Snack Pack can send real footfall or enquiries your way. Local schema won’t guarantee you a spot, but it does help Google decide who’s relevant and reliable.
To make it work best:
- Fill out your Google Business Profile completely.
- Add local business schema to your contact page.
- Keep NAP (Name, Address, Phone number) details consistent everywhere online.
- Collect genuine Google reviews.
Combined, this gives Google a strong signal that your business is active, established and worth recommending.
The easy way to add it
Don’t worry - you don’t need to become a coder to apply markup. If you use WordPress, Wix or Shopify, there are plugins and apps that let you add schema without touching code. (RankMath, Yoast, and Shopify’s built-in product schema all do the job.)
However, it’s worth noting that the free versions of these types of software rarely do anything beyond the very basic markup. This is of limited use. If you are serious about SEO, it is worth investing in the paid versions.
Adding schema using AI and Google Tag Manager
This is really easy once you know how (easy for us to say!) but assumes you have Google Tag Manager and know the basics of usage.
There's no shortage of guides online that show how to add Schema using AI and Google Tag Manager, so if you feel confident and don’t have the budget for software, there are plenty of resources to help you.
Alternatively, Google’s free Markup Helper lets you paste in your page and generate schema manually.
Once it’s added, test it using Google’s Rich Results Test to check everything’s working.
A note of caution
Schema doesn’t guarantee rich results. Search engines when and where to show them. But the clearer your content is, the better chance you have. Just don’t overdo it. Only use schema that matches what’s actually on your page. If you get too clever, Google might reject your markup or even penalise the site.
Why not try it?
Schema is a smart, sustainable win. It helps search engines understand your content, makes your listings more useful, and could lead to more clicks – all with minimal effort and cost. And for small businesses like ours, every click counts. It’s also a key weapon in the battle to be seen in AI results. So why not have a go and let us know how you get on?
Good luck!